2. 贵州医科大学图书馆技术部,贵阳 550004
2. Department of Technology of Library, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, China
Prohibitin基因广泛分布于细菌、植物、酵母及哺乳动物等各种生物细胞中,具有高度的同源性[1]。哺乳动物中研究发现Prohibitin(phb)基因具有明显的抗细胞增殖[2]、抗肿瘤作用[3],其表达产物Prohibitin (PHB)蛋白的氨基酸结构非常保守, 是一类新型的分子伴侣蛋白, 同时具有转录调控作用, 在生物体中发挥着非常重要的作用[4-5]。但到目前为止,昆虫中的Prohibitin基因的生物学功能研究还未见深入报道。Atichat Kuadkitkan等人发现Prohibitin蛋白是登革热2型病毒进入昆虫细胞的受体蛋白质[6]。家蚕中的Prohibitin基因研究证明,Prohibitin基因在家蚕的不同发育时期,发达量存在明显差异,暗示该基因在家蚕的生长发育中有重要的生理功能[7]。课题组在对热诱导处理的家蝇全长cDNA文库中随机EST测序和序列分析发现,其中一候选克隆可能为家蝇Prohibitin基因[8]。根据获得的EST序列,本文在已获得Prohibitin基因全长cDNA序列的基础上,应用生物信息学方法对该基因编码蛋白的基本理化性质、跨膜区、亲疏水性、二级及三级结构、功能域、同源性等进行了分析,拟为该基因的深入研究提供参考和理论依据。
1 材料方法 1.1 材料课题组构建的热诱导家蝇cDNA文库和EST序列。
1.2 Prohibitin基因全长cDNA的获得挑取Prohibitin基因EST序列对应的阳性菌落进行培养并提取质粒,然后进行双向测序。
1.3 序列分析采用ORF程序(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html)查找序列的开放阅读框,用Expasy服务器上ProtParam程序分析蛋白的基本理化性质(http://au.expasy.org/tools/protparam.html)。利用Protscale在线程序[9]对氨基酸序列进行亲疏水性分析(http://au.expasy.org/tools/protscale.html),在线TMHMM 2.0服务器[10]预测蛋白跨膜区(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0),软件SignalP4.0[11]预测蛋白的信号肽(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/signalp),PSORTⅡ软件预测蛋白的亚细胞定位(http://psort.nibb.ac.ja/form2.html),SOPMA软件进行蛋白的二级结构预测(http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html)。
结构域采用NCBI网站上的conserved domains search service在线分析工具预测(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi)。蛋白质三级结构运用Phyre2程序进行(http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index)[12],利用软件MEGA7.0.14进行氨基酸的多重序列比对和系统进化树的绘制[13]。
2 结果分析 2.1 Prohibitin全长cDNA的获得挑取Prohibitin基因的候选克隆进行质粒提取和双向测序,测序结果经Genbank数据库进行Blast比对分析,确为Prohibitin基因的全长cDNA序列。
2.2 序列分析应用NCBI的ORF Finder程序对全长cDNA序列进行开放读码框的查找。结果显示,Prohibitin基因开放读码框为834 bp,共编码277个氨基酸, 序列已提交到GenBank (登录号为: ADT92002.1)。具体氨基酸序列如下:
maaqffnrigqlglgvalvggvvnsalynvdgghravifdrftgvknevtgeg
thffipwvqrpiiydirsqprnvpvvtgskdlqnvnitlrilyrpipdqlpriyti
lgqdydervlpsiapevlkavvaqfdagelitqreivsqrvsdelterakqfgfi
lddisithltfgreftqavemkqvaqqeaekarfvvekaeqqklaaiisaegd
aaaaellaksfaeagdglvelrrieaaediayqlsrsrgvaylpgnqstllnlps
ntlaq
使用ProtParam程序预测该蛋白的分子式为C1366H2182N380O409S2,相对分子质量为30.54 kDa,理论等电点为5.26,不稳定参数为38.39,根据不稳定参数的数值在40以下才是稳定蛋白的标准[6],可推定Prohibitin基因编码的蛋白是稳定蛋白。氨基酸组成中ALA谷氨酸占最大比例(10.8%),带正电荷的残基(ARG+GLU)总数为28个,带负电荷的残基(ASP+GLU)总数34个。
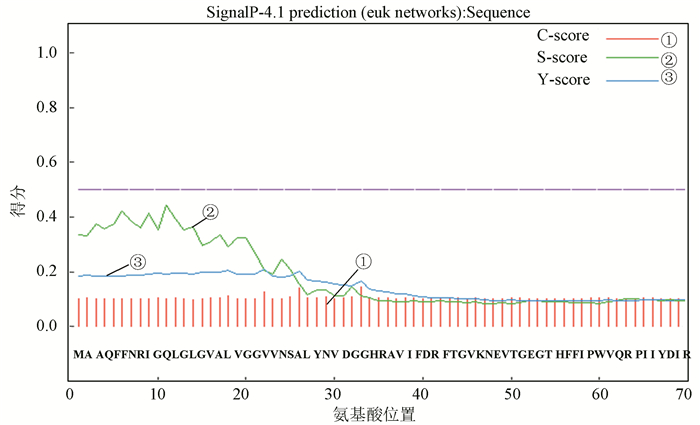
2.4 Prohibitin蛋白的结构域根据蛋白亲疏水性分析结果(见图 1),该蛋白亲水性较强,为亲水蛋白。利用软件TMHMM软件预测得知此蛋白为跨膜蛋白,跨膜区域为9-28(见图 2);图 3表明该蛋白序列无信号肽,不是分泌性蛋白。使用PSORTII软件进行亚细胞定位分析表明,该蛋白定位于细胞质的可能性为56.5%,定位于线粒体、细胞核的可能性分别为13.0%。NCBI网站的conserved domains search service在线分析工具预测结果显示,氨基酸在26-187区域含有一个PHB结构域。该蛋白具有保守的PHB结构域(见图 4)。

|
图 1 Prohibitin蛋白亲疏水性分析 Figure 1 Hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity analysis of prohibitin protein |

|
图 2 Prohibitin蛋白跨膜区预测 Figure 2 Transmenbrane region prediction of Prohibitin protein |
|
图 3 Prohibitin蛋白信号肽预测 Figure 3 Signal peptide prediction of Prohibitin |

|
图 4 Prohibitin蛋白功能域分析 Figure 4 Functional domain analysis of Prohibitin protein |
蛋白的SOPMA软件预测结果如图 5所示,Prohibitin蛋白二级结构元件主要以α-螺旋(Hh)和延伸链结构(Ee))为主(分别占45.49%,23.10%),其次是无规则卷曲(Cc)为22.38%),最少的为β-转角结构(Tt)为9.03%。

|
图 5 Prohibitin蛋白二级结构预测 Figure 5 Secondary structure prediction of Prohibitin 注:h:α-螺旋;e:延伸链;c:无规则卷曲;t:β转角 |
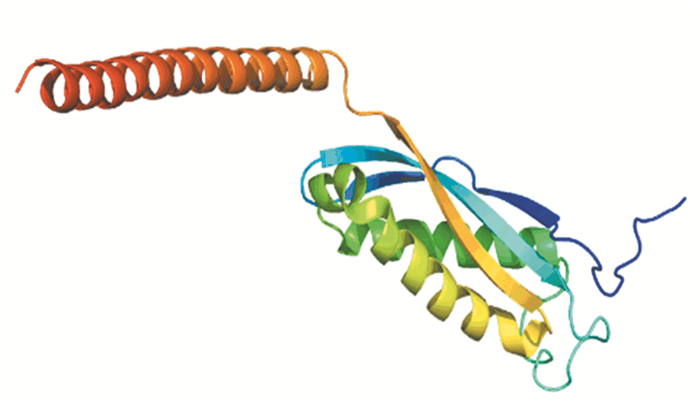
利用在线分析工具Phyre 2对家蝇Prohibitin蛋白氨基酸序列进行三级结构预测。结果见图 6, 结果显示,以c3bk6C结构为模板,Prohibitin蛋白277个氨基酸序列中有156个氨基酸与模板达到99.9%的可信度。
|
图 6 预测的Prohibitin蛋白三级结构 Figure 6 The tertiary structure prediction of Prohibitin |
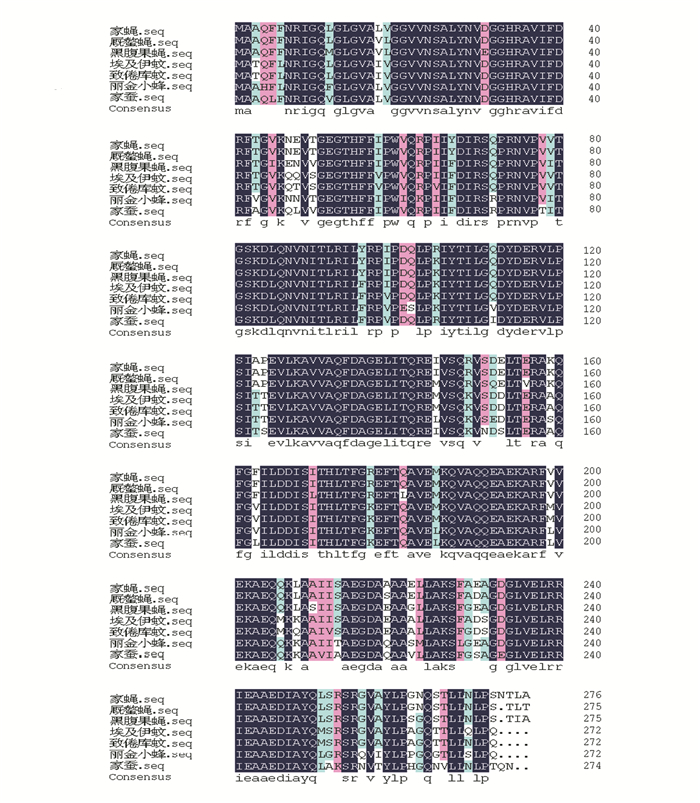
通过Blastp在线同源性比对, Prohibitin蛋白与其他物种同源蛋白序列相似性都比较高,与厩螫蝇(Stomoxys calcitrans) protein l (2)37Cc蛋白序列相似度为97%,与美洲鹦鹉(Amazona aestiva)的prohibitin isoform X1蛋白序列相似度为76%。利用DNAman本地版软件将家蝇Prohibitin蛋白序列与其他昆虫相似蛋白进行同源比对,结果显示(见图 7),昆虫中的Prohibitin蛋白具有较高相似性。
|
图 7 几种昆虫Prohibitin蛋白的多序列比对 Figure 7 Multiple sequence alignment of Prohibitin proteinin different insects |
在NCBI数据库选择厩螫蝇、黑腹果蝇、埃及伊蚊、致倦库蚊、家蚕、丽金小蜂、大蜜蜂等12种昆虫Prohibitin同源蛋白序列,以人类Prohibitin蛋白为外群,构建系统进化树。系统发育分析发现,12种昆虫中的Prohibitin蛋白可分为两大类,其中以家蝇、厩螫蝇、果蝇、埃及伊蚊、致倦库蚊等双翅目昆虫中的Prohibitin蛋白聚为一类,而另一大类则包含膜翅目昆虫亚类和鳞翅目昆虫亚类(见图 8)。

|
图 8 Prohibitin蛋白的系统发育分析 Figure 8 Phylogenetic analysis of Prohibitin protein |
Prohibitin (PHB)是一种进化保守分布广泛的多功能蛋白。然而它具体的功能机制目前还不清楚。为更好的了解PHB蛋白的性质,我们从家蝇幼虫cDNA文库中克隆了Prohibitin基因的cDNA序列,该基因共编码277个氨基酸残基。其编码的蛋白质分子量30.54 kDa,理论等电点为5.26,为稳定蛋白。通过预测,该蛋白具有PHB结构域,具有跨膜区,但不含信号肽,亚细胞定位分析显示该蛋白最大可能存在于细胞质中。该蛋白二级结构以α-螺旋和延伸链为主。同源序列比对及系统发育分析显示该蛋白与其它昆虫的同源蛋白相似性较高。
本研究克隆得到Prohibitin基因的cDNA序列基础上,用生物信息学方法对蛋白序列进行了分析和预测,这些结果将为分子水平上进一步功能研究奠定了基础。
| [1] |
SATO T, SAKAMOTO T, TAKITA KI, et al. The human prohibitin (PHB) gene family and its somatic mutations in human tumors[J]. Genomics, 1993, 17(3): 762–764.
DOI:10.1006/geno.1993.1402 ( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
CHOWDHURY I, THOMAS K, THOMPSON W E. Prohibitin (PHB) roles in granulosa cell physiology[J]. Cell Tissue Research, 2016, 363(1): 19–29.
DOI:10.1007/s00441-015-2302-9 ( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
XU Y, YANG W, SHI J, et al. Prohibitin 1 regulates tumor cell apoptosis via the interaction with X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein[J]. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, 2016, 8(3): 282–285.
DOI:10.1093/jmcb/mjw018 ( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
ZHONG X, SONG X, WANG N, et al. Molecular identification and characterization of prohibitin from Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Parasitol Research, 2016, 115(2): 897–902.
DOI:10.1007/s00436-015-4846-8 ( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
ANDE S R, NGUYEN K H, NYOMBA B L, et al. Prohibitin in adipose and immune functions[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 27(8): 531–541.
DOI:10.1016/j.tem.2016.05.003 ( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
KUADKITKAN A, WIKAN N, FONGSARAN C, et al. Identification and characterization of prohibitin as a receptor protein mediating DENV-2 entry into insect cells[J]. Virology, 2010, 406(1): 149–161.
DOI:10.1016/j.virol.2010.07.015 ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
LV Z, ZHANG X, LIU L, et al. Characterization of a gene encoding prohibitin in silkworm, Bombyx mori[J]. Gene, 2012, 502(2): 118–24.
DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2012.03.035 ( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
刘红美, 张洁, 王贇, 等. 热胁迫后家蝇幼虫cDNA文库构建与随机EST测序分析[J]. 免疫学杂志, 2010, 26(9): 772–775.
LIU hongmei, ZHANG jie, WANG yun, et al. Construction of c DN A library from Musca domestica L. larvae following heat stress and the EST sequencing[J]. Immunological Journal, 2010, 26(9): 772–775.
DOI:10.13431/j.cnki.immunol.j.20100183 ( 0) 0)
|
| [9] |
GASTEIGER E, HOOGLAND C, GATTIKER A, et al. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server; (In) John M. Walker (ed): The proteomics protocols handbook. New York City: Humana Press, 2005 : 571 -607.
( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
OLOF E, SREN B, GUNNAR H, et al. Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP, and related tools[J]. Nature Protocols, 2007, 2(4): 953–971.
DOI:10.1038/nprot.2007.131 ( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
THOMAS N P, SOREN B, GUNNAR H, et al. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(1): 785–786.
DOI:10.1038/nmeth.1701 ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
KELLEY L A, MEZULIS S, YATES C M, et al. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis[J]. Nature Protocols, 2015, 10(6): 845–858.
DOI:10.1038/nprot.2015.053 ( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K. 7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2016, 33(7): 1870–1874.
DOI:10.1093/molbev/msw054 ( 0) 0)
|
 2016, Vol. 14
2016, Vol. 14

