microRNAs(MiRNAs)是一类长约18-25个核苷酸的非编码RNA,与mRNA转录本的3’非翻译区(3’-UTR)结合,可以对靶基因的表达进行调控[1]。它们对各种重要的生物学过程具有调控作用,如细胞发育、细胞增殖、细胞分化及细胞凋亡等有关[2],因此准确预测miRNA的靶基因并对其靶基因进行系统的生物学分析是研究其作用机制的重要环节。本研究前期为了探讨miRNAs在三邻甲苯基磷酸酯(Tri-o-cresyl phosphate,TOCP)诱发神经细胞自噬中的作用机制,以人神经母细胞瘤细胞SK-N-SH细胞为体外细胞自噬模型,应用miRNA基因芯片、RT-PCR等实验技术检测了自噬相关miRNA表达情况。综合芯片和荧光实时定量PCR的结果,筛选出了miR-210-5p显著性差异表达的自噬基因。
Hsa-miR-210-5p属于miR-210基因家族,定位于人11号染色体568 150-568 171。研究表明低氧诱导的miR-210参与细胞循环、细胞分化、DNA修复、细胞凋亡、膜转运、氧化应激/糖酵解等调控信号通路,可作为非小细胞癌、乳腺癌、胰腺癌、肺细胞癌、食管鳞状细胞癌等癌症的诊断参考指标和预后指标[3],其过表达与昼夜节律过程、神经元发育、GTP酶信号转导和光感受相关的途径有关[4],但目前国内外对miR-210-5p的报道较少。本研究运用生物信息学分析,预测hsa-miR-210-5p的靶基因,绘制韦恩图得靶基因集合,并对其靶基因集合进行蛋白质互作网络分析、GO(Gene Ontology)分析和KEGG Pathway(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)分析预测结果中的靶基因集合作用机制,并注释其靶基因的生物学功能,为展开miR-210-5p的靶基因鉴定及生物学功能研究提供理论基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 miR-210-5p序列的保守性分析使用miRbase[5](http://www.mirbase.org/)、RNAcentral(https://rnacentral.org/)数据库在线查找各物种已知成熟miR-210-5p碱基序列,对比分析miR-210-5p序列在各物种间的保守性。
1.2 miR-210-5p靶基因的预测利用miRDB[5](www.mirdb.org/),TargetSc-an[5](http://www.targetscan.org/)和DIANA TO-OLS[5](http://diana.imis.athena-innovation.gr/) 3个在线数据库预测miR-210-5p的靶基因,用在线软件Veney 2.1.0 (http//bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/Venny/index.html)画韦恩图,得到3个数据库预测结果的交集,该交集为靶基因集合,以降低假阳性率。
1.3 预测靶基因集合编码蛋白质之间的相互作用将该靶基因集合使用String 11.0(Search Tool for the retrieval of interacting genes)在线数据库(https://string-db.org/)分析,绘制互作网络邻接编码蛋白数目柱状图,再利用Cytoscape_v3.6.1绘制靶基因集合编码蛋白质之间相互作用(protein-protein interaction, PPI)网络图。
1.4 miR-210-5p靶基因的GO分析使用DAVID(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/)数据库对预测到的miR-210-5p靶基因集合进行GO功能注释,以人的所有基因为背景基因,显著性阈值取P < 0.05,获得相对hsa-miR-210-5p具有统计学意义的GO分析。GO分析由细胞组分(Cellular component)、分子功能(Molecular function)、生物调节(Biological process)3个部分组成。用R软件绘制miR-210-5p靶基因交集的GO功能注释图。
1.5 miR-210-5p靶基因的KEGG Pathway分析使用DAVID(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/)数据库对预测到的miR-210-5p靶基因集合进行KEGG Pathway富集分析,以人的所有基因为背景基因,显著性阈值取P < 0.05,获得相对于hsa-miR-210-5p具有统计学意义的基因集合信号转导通路。用R软件绘制miR-210-5p靶基因交集的KEGG Pathway富集通路图。
2 结果分析 2.1 miR-210-5p参与的疾病miR-210-5p在骨质疏松[6]、骨关节炎[7]、自闭症障碍[8],心血管疾病[9]中起上调作用(见表 1)。
| 表 1 miR-210-5p调控靶基因参与人类的部分疾病 Table 1 miR-210-5p target genes involved in parts of human diseases |
使用RNAcentral和miRBase数据库进行对比分析,可知其基因序列号为MIMAT002475,定位于11号染色体568 150-568 171。对猕猴(mml)、小鼠(mmu)、褐家鼠(rno)等8个物种对比分析,可知hsa-miR-210-5p的成熟碱基序列“agccccugcccaccgcacacug”在各物种间高度保守(见表 2)。
| 表 2 各物种miR-210-5p的成熟碱基序列 Table 2 Mature base sequences of miR-210-5p of various species |
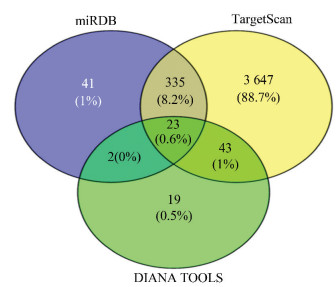
使用数据库miRDB,TargetScan和DIANA TOOLS预测miR-210-5p的靶基因,预测的个数分别为401、4 048和87,然后用在线软件Veney 2.1.0可得三个数据库预测靶基因的交集23个,占各预测软件预测靶基因总和的0.6%(见图 1)。
|
图 1 miR-210-5p的预测靶基因个数 Figure 1 Prediction of the number of target genes for miR-210-5p |
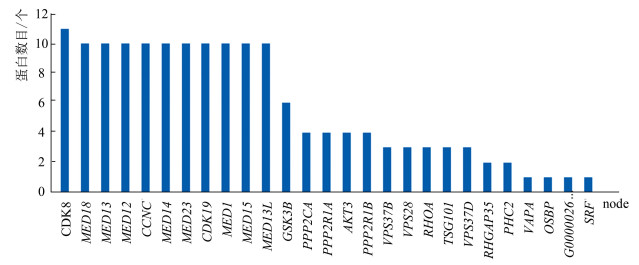
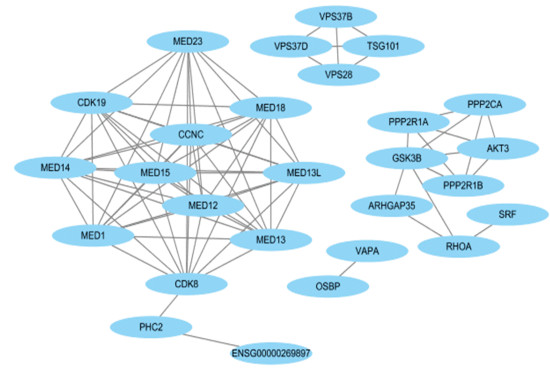
将三个数据库得到的靶基因集合使用String 11.0数据库分析,绘制出互作网络邻接编码蛋白数目柱状图(见图 2)。结果显示,靶基因CDK8、MED18、MED13、MED12、CCNC、MED14、MED23、CDK19、MED1、MED15和MED13L的编码蛋白质所占比重较大。运用Cytoscape_ v 3.6.1软件,绘制出PPI网络图(见图 3)。结果表明,miR-210-5p的靶基因集合编码蛋白质之间的相互作用关系较复杂,有10个编码蛋白质之间的互作关系较稳定。
|
图 2 互作网络邻接编码蛋白数目柱状图 Figure 2 Adjacency coding protein number histogram of interaction networks |
|
图 3 miR-210-5p预测靶基因集合所编码蛋白质之间的相互作用 Figure 3 Protein-protein interaction network of the target genes of miR-210-5p |
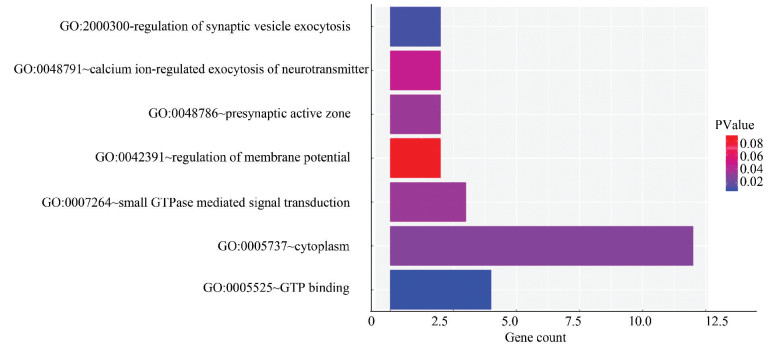
使用DAVID数据库对预测到的miR-210-5p靶基因集合进行GO功能注释,以人的所有基因为背景基因(P < 0.05),可得其主要富集的细胞组分是细胞质、细胞浆和突触前活动区;分子功能是参与鸟苷酸合成;参与突触小泡胞吐的调控、鸟苷酸蛋白介导的信号转导、钙离子调节的神经递质胞吐和膜电位调节等生物学过程(见表 3),用R软件绘制miR-210-5p靶基因交集的GO功能注释图(见图 4)。
| 表 3 miR-210-5p靶基因交集的GO功能注释 Table 3 GO functional annotation for intersection of miR-210-5p target genes |
|
图 4 miR-210-5p靶基因交集GO功能注释 Figure 4 GO functional annotation for intersection of miR-210-5p target gene |
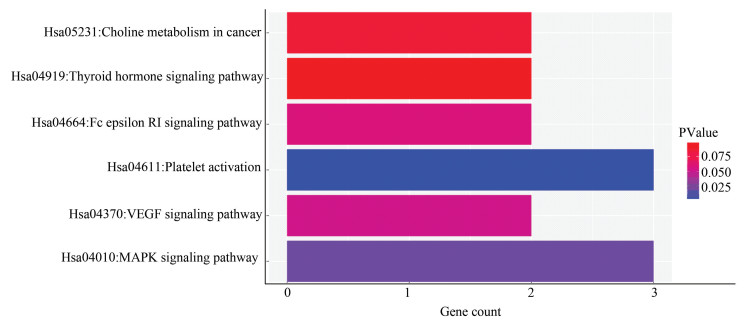
使用DAVID数据库对预测到的miR-210-5p靶基因集合进行KEGG Pathway分析,以人的所有基因为背景基因(P < 0.05),可得miR-210-5p的靶基因集合参与血小板活化、MAPK信号通路、VEGF信号通路、癌症通路、甲状腺激素信号通路等(见表 4),用R软件绘制miR-210-5p靶基因交集的KEGG pathway通路图(见图 5)。
| 表 4 miR-210-5p靶基因交集的KEGG Pathway分析 Table 4 KEGG pathway analysis for intersection of miR-210-5p target genes |
|
图 5 miR-210-5p靶基因交集的KEGG Pathway分析 Figure 5 KEGG pathway analysis for intersection of miR-210-5p target genes |
miR-210在肿瘤、心血管系统,神经系统疾病中起发挥重要作用。miR-210能上调Kaposi肉瘤相关的疱疹病毒和感染[11]、慢性鼻-鼻窦炎鼻息肉患者黏膜黏蛋白0型聚糖生物合成途径[12]、人骨肉瘤[13],小鼠感觉轴突再生[14]和脊髓再生[15],可通过在动脉粥样硬化的情况下直接靶向PDK1诱导内皮细胞凋亡有下调作用[16],能抑制滋养层细胞侵袭,是先兆子痫的血清生物标志物[17]。hsa-miR-210-5p属于miR-210基因家族,miRNA-210-5p在神经功能调节中报道较少。
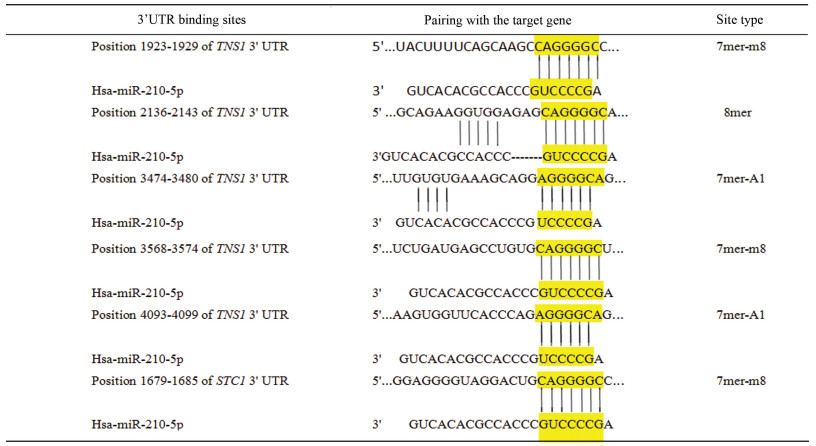
考虑到靶基因预测过程中miRNA与靶基因结合位点的序列匹配、mRNA与miRNA双链特异结合的热稳定性及序列的保守性等因素, 采用miRDB、TargetScan,DIANA TOOLS三个数据库对miR-210-5p靶基因进行预测,得到了可信度较高的靶基因集合,进行编码蛋白质互作分析,GO分析和KEGG pathway分析。研究发现miR-210-5p能促进成骨细胞的分化[6]、成骨细胞胞外体的表达[7]、调节钙通道[8]、促进细胞缺氧凋亡[9]、能结合位点突变,降低荧光酶活性[10]、参与细胞的免疫反应[18]、阻断胚状体细胞扩增[19]、对孕妇发生先兆子痫[20]、肾细胞癌[21],在副溶血性孤菌感染的文昌鱼的免疫反应中起着重要调节作用[22]。提示miR-210-5p可能调控癌症的发生与转归、钙离子信号通路、血小板活化,免疫系统和神经系统等生物学过程。miR-210-5p靶向TNS1和STC1调节缺氧时心肌细胞发生的变化,进而调控心血管疾病[9]。在TargetScan Human 7.2可查到基因TNS1与miR-210-5p种子区域的配对类型为7mer-m8、7mer-A1和8mer,基因STC1与miR-210-5p种子区域的配对类型为7mer-m8,并且它们与miR-210-5p非种子区域3'端存在不同长度的互补位型(见表 5)。miR-210-5p种子区域与TNS1和STC1基因的3'UTR完全匹配可以增强miR-210-5p对TNS1和STC1基因的沉默效果,故可用miR-210-5p与TNS1和STC1基因的高特异性来研究miR-210-5p对TNS1和STC1基因富集的疾病通路如心血管疾病的治疗是具有发展意义的。
| 表 5 TNS1和STC1基因3'UTR结合miR-210-5p的位点 Table 5 3'UTR sequences of TNS1 and STC1 targeted by miR-210-5p |
选用三种数据库预测miR-210-5p靶基因,取其交集分析,不能避免预测结果的假阳性,需通过实验验证该靶基因集合里23个靶基因为miR-210-5p的靶基因,进一步探讨目标靶基因3’UTR结合miR-210-5p的位点及其具体分子机制来降低假阳性率。运用生物信息学分析方法,较全面的分析了hsa-miR-210-5p所参与的生物学过程,为后续研究提供了方向。
| [1] |
JIANG Hui, WANG Jianxin, LI Min, et al. miRTRS:A recommendation algorithm for predicting miRNA targets[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2018, 14(8): 1545-5963. DOI:10.1109/TCBB.2018.2873299 (  0) 0) |
| [2] |
JI Jia, RONG Yuan, LUO Changliang, et al. Up-regulation of hsa-miR-210 promotes venous metastasis and predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Frontiers in Oncology, 2018, 8(569): 1-11. DOI:10.3389/fonc.2018.00569 (  0) 0) |
| [3] |
文娟, 罗招阳, 左建宏. 低氧相关microRNA-210在实体肿瘤研究中的进展[J]. 中南医学科学杂志, 2014, 42(01): 1-5+65. WEN Juan, LUO Zhaoyang, ZUO Jianhong. Progress of hypoxia-related microRNA-210 in the study of solid tumors[J]. Medical Science Journal of Central South China, 2014, 42(01): 1-5+65. DOI:10.15972/j.cnki.43-1509/r.2014.01.003 (  0) 0) |
| [4] |
PAOLA C, ALBERTO B, FEDERICA S, et al. Modulation of miR-210 alters phasing of circadian locomotor activity and impairs projections of PDF clock neurons in Drosophila melanogaster[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2018, 14(7): e1007500. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1007500 (  0) 0) |
| [5] |
程爽, 郭茂祖, 武雪剑. microRNA靶基因预测算法的研究与发展[J]. 智能计算机与应用, 2018, 8(1): 1-5+13. CHENG Shuang, GUO Maozu, WU Xuejian. Research and development of microRNA target gene prediction algorithm[J]. Intelligent Computer and Applications, 2018, 8(01): 1-5+13. (  0) 0) |
| [6] |
LIU Xiaodong, CAI Feng, LIU Liang, et al. MicroRNA-210 is involved in the regulation of postmenopausal osteoporosis through promotion of VEGF expression and osteoblast differentiation[J]. Biological Chemistry, 2015, 396(4): 339-347. DOI:10.1515/hsz-2014-0268 (  0) 0) |
| [7] |
刘博豪, 吴鹏飞, 梅林, 等. 骨关节炎患者成骨细胞胞外体miRNAs表达谱的差异[J]. 中南大学学报, 2018, 43(12): 1294-1300. LIU Bohao, WU Pengfei, MEI Lin, et al. Differential expression of exosomal miRNAs in osteoblasts in osteoarthritis[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 43(12): 1294-1300. DOI:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.12.003 (  0) 0) |
| [8] |
TATYANA M K, NIKOLAY T P, IVAN S I, et al. Profiling of circulating serum microRNAs in children with autism spectrum disorder using stem-loop qRT-PCR Assay[J]. Folia Medica, 2017, 59(1): 43-52. DOI:10.1515/folmed-2017-0009 (  0) 0) |
| [9] |
LEE W, TSAI M, CHANG W, et al. Deduction of novel genes potentially involved in hypoxic AC16 human cardiomyocytes using next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics approaches[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2018, 42(5): 2489-2502. DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3851 (  0) 0) |
| [10] |
REN Zhenxing, YU Junlong, WU Zimei, et al. MicroRNA-210-5p contributes to cognitive impairment in early vascular dementia rat model through targeting snap25[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 2018, 11(388): 1-13. DOI:10.3389/fnmol.2018.00388 (  0) 0) |
| [11] |
CORALIE V, DAVID A D, SHEWIT S T, et al. RNA sequencing reveals that kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection mimics hypoxia gene expression signature[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2017, 13(1): e1006143. DOI:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006143 (  0) 0) |
| [12] |
XUAN Lijia, LUAN Ge, WANG Yue, et al. microRNAs regulating mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis and transforming growth factor β signaling pathways in nasal mucosa of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Northern China[J]. International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, 2019, 9(1): 106-113. DOI:10.1002/alr.22230 (  0) 0) |
| [13] |
PAN Yue, LU Lingyun, CHEN Junquan, et al. Identification of potential crucial genes and construction of microRNA-mRNA negative regulatory networks in osteosarcoma[J]. Hereditas, 2018, 155(21): 1-8. DOI:10.1186/s41065-018-0061-9 (  0) 0) |
| [14] |
HU Yiwen, JIANG Jingjing, GAO Yan, et al. MicroRNA-210 promotes sensory axon regeneration of adult mice in vivo and in vitro[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2016, 622: 61-66. DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.034 (  0) 0) |
| [15] |
SATOSHI U, NAOSUKE K, HIKMAT H, et al. Administration of microRNA-210 promotes spinal cord regeneration in mice[J]. Spine, 2014, 39(14): 1099-1107. DOI:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000356 (  0) 0) |
| [16] |
LI Ying, YANG Chunyan, ZHANG Lili, et al. MicroRNA-210 induces endothelial cell apoptosis by directly targeting PDK1 in the setting of atherosclerosis[J]. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 2017, 22(3): 1-13. DOI:10.1186/s11658-017-0033-5 (  0) 0) |
| [17] |
LAUREN A, ANTHONY O O-G, NADAV S, et al. miR-210 inhibits trophoblast invasion and is a serum biomarker for preeclampsia[J]. The American Journal of Pathology, 2013, 183(5): 1437-1445. DOI:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.07.021 (  0) 0) |
| [18] |
AHN S, JEONG E, MIN J W, et al. Identification of genes dysregulated by elevation of microRNA-210 levels in human trophoblasts cell line, Swan 71[J]. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology, 2017, 78(5): 1-9. DOI:10.1111/aji.12722 (  0) 0) |
| [19] |
ZHENG Guoxing, TAO Ye, YU Wei, et al. Brief report:SRF-dependent MiR-210 silences the sonic hedgehog signaling during cardiopoesis[J]. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio), 2013, 31(10): 2279-2285. DOI:10.1002/stem.1464 (  0) 0) |
| [20] |
CARINE M, LINDA T, SILVIA B, et al. Dysregulated circulating miRNAs in preeclampsia[J]. Biomedical Reports, 2016, 5(6): 686-692. DOI:10.3892/br.2016.779 (  0) 0) |
| [21] |
YING Guanghui, WU Ruilan, XIA Min, et al. Identification of eight key miRNAs associated with renal cell carcinoma:A meta-analysis[J]. Oncology Letters, 2018, 16(5): 5847-5855. DOI:10.3892/ol.2018.9384 (  0) 0) |
| [22] |
JIN Ping, LI Shengjie, SUN Lianjie, et al. Transcriptome-wide analysis of microRNAs in Branchiostoma belcheri upon Vibrio parahemolyticus infection[J]. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2017, 74: 243-252. DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2017.05.002 (  0) 0) |
 2020, Vol. 18
2020, Vol. 18